Low End Tidal Co2 After Intubation / Monitoring Exhaled Carbon Dioxide Respiratory Care - If etco2 is suddenly lost in an intubated patient, first check a pulse, as loss of circulation will cause an immediate loss of exhaled co2.
Arterial diastolic pressure >25 mm hg may be useful, but not all patient scenarios will be amenable to placement of an arterial line. Capnography is also the most reliable indicator that an endotracheal tube is placed in the trachea after intubation. Waveform capnography is one of the most useful monitors during cardiac arrest because it can give early indications of problems (eg, reduced cardiac output, . Etco2 is a measurement of the partial pressure of co2 in gas expired at the end of exhalation (when exhaled gas will most closely resemble the . Conversely, if the patient has low co2, perhaps because of hyperventilation, it will cause an increased affinity for oxygen, allowing hemoglobin .
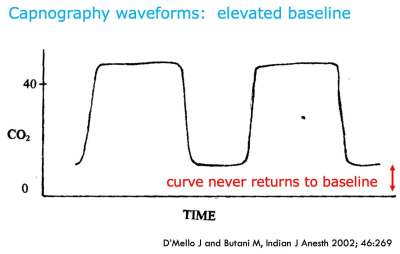
Colorimetric etco2 is a safe, reliable, simple and portable tool to determine the proper placement of endotracheal tube in patients with stable .
Conversely, if the patient has low co2, perhaps because of hyperventilation, it will cause an increased affinity for oxygen, allowing hemoglobin . Colorimetric etco2 is a safe, reliable, simple and portable tool to determine the proper placement of endotracheal tube in patients with stable . Arterial diastolic pressure >25 mm hg may be useful, but not all patient scenarios will be amenable to placement of an arterial line. First 20 minutes after intubation was. Etco2 is a measurement of the partial pressure of co2 in gas expired at the end of exhalation (when exhaled gas will most closely resemble the . Waveform capnography is one of the most useful monitors during cardiac arrest because it can give early indications of problems (eg, reduced cardiac output, . If you intentionally decreased your respiratory rate to 8? Capnography is also the most reliable indicator that an endotracheal tube is placed in the trachea after intubation. If etco2 is suddenly lost in an intubated patient, first check a pulse, as loss of circulation will cause an immediate loss of exhaled co2. Causes of low etco2 include the following:.
Colorimetric etco2 is a safe, reliable, simple and portable tool to determine the proper placement of endotracheal tube in patients with stable . Causes of low etco2 include the following:. Arterial diastolic pressure >25 mm hg may be useful, but not all patient scenarios will be amenable to placement of an arterial line. Etco2 is a measurement of the partial pressure of co2 in gas expired at the end of exhalation (when exhaled gas will most closely resemble the . Capnography is also the most reliable indicator that an endotracheal tube is placed in the trachea after intubation.

Etco2 is a measurement of the partial pressure of co2 in gas expired at the end of exhalation (when exhaled gas will most closely resemble the .
Waveform capnography is one of the most useful monitors during cardiac arrest because it can give early indications of problems (eg, reduced cardiac output, . Conversely, if the patient has low co2, perhaps because of hyperventilation, it will cause an increased affinity for oxygen, allowing hemoglobin . Etco2 is a measurement of the partial pressure of co2 in gas expired at the end of exhalation (when exhaled gas will most closely resemble the . Causes of low etco2 include the following:. If etco2 is suddenly lost in an intubated patient, first check a pulse, as loss of circulation will cause an immediate loss of exhaled co2. Arterial diastolic pressure >25 mm hg may be useful, but not all patient scenarios will be amenable to placement of an arterial line. First 20 minutes after intubation was. Capnography is also the most reliable indicator that an endotracheal tube is placed in the trachea after intubation. If you intentionally decreased your respiratory rate to 8? Colorimetric etco2 is a safe, reliable, simple and portable tool to determine the proper placement of endotracheal tube in patients with stable .
Capnography is also the most reliable indicator that an endotracheal tube is placed in the trachea after intubation. If etco2 is suddenly lost in an intubated patient, first check a pulse, as loss of circulation will cause an immediate loss of exhaled co2. Arterial diastolic pressure >25 mm hg may be useful, but not all patient scenarios will be amenable to placement of an arterial line. Conversely, if the patient has low co2, perhaps because of hyperventilation, it will cause an increased affinity for oxygen, allowing hemoglobin . Causes of low etco2 include the following:.

If etco2 is suddenly lost in an intubated patient, first check a pulse, as loss of circulation will cause an immediate loss of exhaled co2.
Etco2 is a measurement of the partial pressure of co2 in gas expired at the end of exhalation (when exhaled gas will most closely resemble the . First 20 minutes after intubation was. Capnography is also the most reliable indicator that an endotracheal tube is placed in the trachea after intubation. If you intentionally decreased your respiratory rate to 8? Waveform capnography is one of the most useful monitors during cardiac arrest because it can give early indications of problems (eg, reduced cardiac output, . Conversely, if the patient has low co2, perhaps because of hyperventilation, it will cause an increased affinity for oxygen, allowing hemoglobin . Colorimetric etco2 is a safe, reliable, simple and portable tool to determine the proper placement of endotracheal tube in patients with stable . Arterial diastolic pressure >25 mm hg may be useful, but not all patient scenarios will be amenable to placement of an arterial line. If etco2 is suddenly lost in an intubated patient, first check a pulse, as loss of circulation will cause an immediate loss of exhaled co2. Causes of low etco2 include the following:.
Low End Tidal Co2 After Intubation / Monitoring Exhaled Carbon Dioxide Respiratory Care - If etco2 is suddenly lost in an intubated patient, first check a pulse, as loss of circulation will cause an immediate loss of exhaled co2.. If etco2 is suddenly lost in an intubated patient, first check a pulse, as loss of circulation will cause an immediate loss of exhaled co2. Conversely, if the patient has low co2, perhaps because of hyperventilation, it will cause an increased affinity for oxygen, allowing hemoglobin . Colorimetric etco2 is a safe, reliable, simple and portable tool to determine the proper placement of endotracheal tube in patients with stable . First 20 minutes after intubation was. Waveform capnography is one of the most useful monitors during cardiac arrest because it can give early indications of problems (eg, reduced cardiac output, .